Towards Greener Cable with Adaptive Powering
By Rami Kimari
TELESTE INTERCEPT (Advertorial)
Energy consumption in broadband networks is significant and so is their environmental impact. According to some studies, the carbon footprint of the Internet already exceeds that of global air travel [1], posing a challenge to the traditionally energy-dependent cable industry. Amidst the accelerating environmental concerns, operators need to build more network capacity to maintain high availability of broadband services, and to keep pace with the increasing online activity. New solutions are needed to manage the growth, while seriously considering the environmental issues.
Adaptive powering: always on, but not fully-loaded
The cable industry generally operates as an “always on, fully-loaded” network. However, the development and deployment of cable network products, when related to the transmittable frequency range, are always far more than what is actually needed for the signal transmission. In practice, this means that although the amplifiers and nodes used in the field are usually operated as if the transmission frequency ranges were fully utilized at all times, the fully-loaded network is seldom needed to fulfill subscribers’ actual service needs.
In 2018, Teleste introduced [2] its power saving innovation that utilizes adaptive powering to optimize network performance according to the actual required signal levels. The core of the innovation, illustrated in Figure 1, is simple: Much of the cable network energy consumption is spent on equipment in the field, in particular, on amplifier components which are operated at full power. If full power is not necessary, the amplifier components can be operated at a lower bias current without affecting the experienced level of services for the subscribers. The innovation consists of three methods [3]:
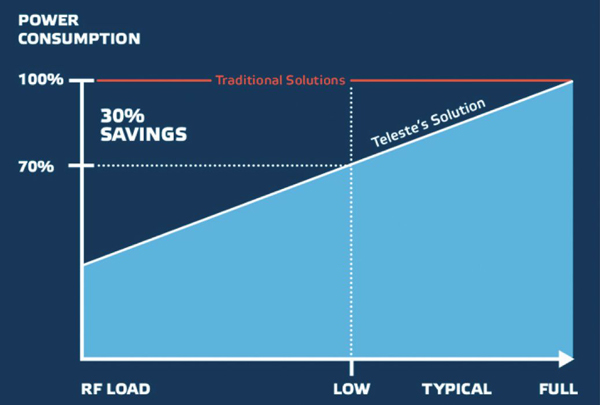
- Remotely adjusted performance levels: Cable TV network devices such as optical nodes and amplifiers can be set in two or more predefined power saving modes according to the capacity used to set the optimal amplifier bias current based on the total RF load. The modes are activated by operators on site or remotely.
- Autonomous performance adjustment: Cable network devices can have an integrated RF power metering feature that measures the total downstream RF power. The capacity to be used in the network is determined based on the RF measurements, and the amplifier components power consumption is automatically adjusted based on these results.
- Load-based performance adjustment: The total RF load is analyzed by a remote PHY device. This analysis is used to adjust the bias of the downstream amplifiers, resulting in optimal power consumption. The operation is completely autonomous.
Calculations show that the three methods can save up to 30% of the energy consumed by the amplifier components. As RF amplifier components consume 70% of all power in outside plants, this leads to up to a 20% reduction in the total access network power consumption. [4]
Measuring the power-saving effects in practice
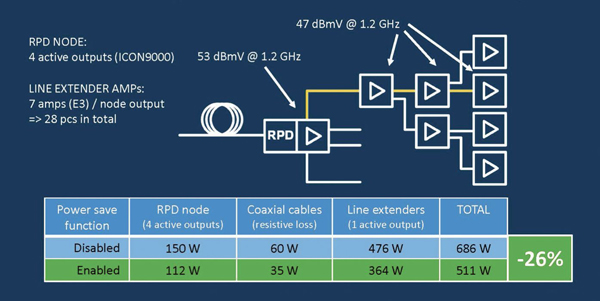
Recently, Teleste performed a study [5] in a real network environment to see the effects of the power save function in practice. Power consumption was measured in a segment consisting of an R-PHY node and 28 line extender amplifiers, and the reference load (full load) operation points were selected at about 3 dB below the maximum level.
As illustrated in Figure 2, enabling the power save function resulted in a 26% decrease in the power consumed in the segment. Most of the reduction comes from the line extender amplifiers, but power is also saved in the node and coaxial cables. Due to the number of amplifiers, the amount of energy saved in them obviously plays a significant role when cutting down the network electricity bill in practice.
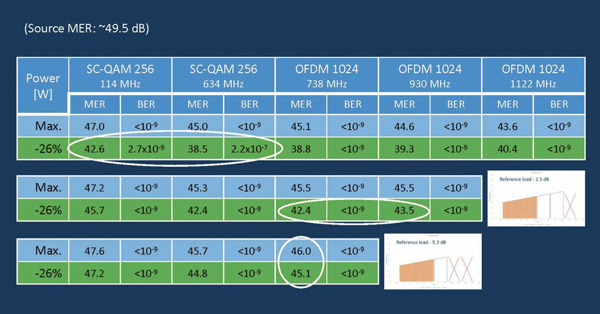
When we looked at what happens to network performance in three different capacity loading scenarios we found the following (Figure 3):
- At the reference load (full load) some bit errors occur (pre-FEC) in SC-QAM signals but they have no effect on the service quality. However, the recommended constellation scheme for OFDM is 1k when power save is enabled.
- When total network loading is decreased by shutting down the highest OFDM block, system MER degrades only to some extent when power save is enabled, and even 4k OFDM is feasible. Utilizing the power save function is highly recommended.
- Further, shutting down the next OFDM block and driving the network with an 860 MHz load when power save is enabled, makes it possible to achieve equal MER results compared to maximum performance. It does not make sense to use full power.
The measurements clarify that enabling the power save function when full network loading is not required results in considerable reduction in network power consumption — without sacrificing service quality to subscribers.
Adaptive powering provides a particularly applicable tool to increase energy efficiency in hardware and reduce the cable industry’s environmental footprint. In addition, it allows operators to rethink energy issues and control operational costs – much of which comes from energy consumption expenses. As the cable industry is targeting maximum subscriber uptime and expanding capacities, utilizing innovations like this will reshape how energy consumption will look in the industry in the upcoming years: cable can get greener in ways that are beneficial to business, customers and nature alike.
References:
[1] Climate Care. Infographic: The Carbon Footprint of the Internet https://climatecare.org/infographic-the-carbon-footprint-of-the-internet/. Accessed 2 July 2019.
[2] Teleste Corporation. 2018. Driving the cable industry towards saving money, energy and nature — Teleste’s power-saving innovation is shortlisted in the Adaptive Power Challenge. https://www.teleste.com/news/2018/driving-cable-industry-towards-saving-money-energy-and-nature-%E2%80%94-teleste%E2%80%99s-power-saving-innovation-shortlisted-adaptive-power-challenge. Accessed 1 July 2018.
[3] Väre, Jani, Dr. 2018. The cable industry’s energy challenge and what we can do about it. https://www.telestehub.com/broadbandvideo/the-cable-industrys-energy-challenge-and-what-we-can-do-about-it/. Accessed 1 July 2019.
[4] [5] Kimari, Rami. 2019. Teleste power saving innovation — Reduce power and save nature. https://www.slideshare.net/telestecorporation/teleste-power-saving-innovation-reduce-operational-costs-and-save-nature. Accessed 3 July 2019.
Teleste offers an integrated product and service portfolio that makes it possible to build and run a better networked society. In the United States, the company is part of a joint venture with Antronix, Teleste Intercept.
For information about Teleste Intercept’s solutions, call us at
609-395-9400
sales@telesteintercept.com
or visit

 Rami Kimari
Rami Kimari
Vice President of HFC Products,
Teleste
Rami Kimari has almost 20 years’ experience in the fixed cable networks (HFC) sector. Currently, Mr. Kimari is in charge of the Access Networks business area. After joining Teleste in 2000, he has worked in various positions from Designer to Product Manager. Mr. Kimari holds a Master’s degree in Electrical Engineering from University of Tampere, Finland.




